What is Backup?
Backup is the process of copying real or virtual files or databases to a backup place in the event of equipment failure or disaster. Backing up data is critical to a good disaster recovery strategy.
In the case of flawed software, data corruption, hardware failure, hostile hacking, user mistake, or other unforeseen circumstances, businesses back up data they perceive to be vulnerable. Backups take a snapshot in time and synchronize it, which is subsequently used to restore data to its former condition.
Backup and recovery testing investigates an organization’s data security and replication procedures and technologies. The goal is to ensure that data can be retrieved quickly and reliably when needed. File restoration is the process of retrieving backed-up data files.
Although the terms data backup and data protection are sometimes used interchangeably, data protection includes the larger aims of business continuity, data security, information lifecycle management, and malware and computer virus avoidance.
Benefit of Data Backup
- To prevent data loss both intentional and unintentional
- To recover old data because there is a problem with editing the current data or invalid files and want to return to the old data previously
- Prevent storage media damage If the storage media is damaged It will be very difficult to recover data back.
- Prevent virus infection and theft of information from the hackerเพื่อป้องกันการทำข้อมูลสูญหาย ทั้งที่ตั้งใจและไม่ตั้งใจ
The importance of data backup
Because they protect against data loss, data backups are one of the most crucial infrastructure components in any firm. Backups allow you to restore deleted files or recover files that have been mistakenly overwritten.
Furthermore, backups are typically the greatest option for recovering from a ransomware attack or a large data loss catastrophe, such as a data centre fire.
What data should be backed up and how often should it be done?
Critical databases and associated line-of-business applications are backed up. Predefined backup rules dictate how often data is backed up and how many duplicate copies (known as replicas) are necessary, as well as service-level agreements (SLAs) that dictate how quickly data must be restored.
A thorough data backup should be scheduled at least once a week, preferably during weekends or off-business hours, according to best practises. Enterprises generally arrange a series of differential or incremental data backup tasks to augment weekly full backups by backing up only the data that has changed since the last full backup.
The evolution of backup media
Organizations often back up important data to specially designed backup devices, such as tape or disks, and use custom backup software. They may be integrated into the same device (Backup Appliance) or run on separate servers. The process of copying data to disk devices is handled.
The backup software manages the processes. such as deduplication , which reduces the amount of space or storage space. Backup software also enforces policies that control the frequency of backups. Number of copies made and where to store backup data according to the specified backup policy (Backup Plan)
Tape
Before disks became the primary backup medium in the early 2000s, most organizations used tape libraries to store data center backups on tape. Tapes are still mainly used today for archival data that do not require rapid recovery. Some organizations have adopted the practice of using removable disk drives instead of tape. But the basic idea of backing up to removable media remains the same.
Disk
Disk backup enables organizations to continuously and quickly protect their data. Prior to disk backup Organizations tend to create only one backup per day at night. Previously, nightly backups were full backups over time. The backup file is bigger. while the duration for backups remains the same or decreases. This forces many organizations to create incremental or differential backups each day instead.
Virtual Tape Library (VTLs)
The earliest disk backup systems were called Virtual tape libraries (VTLs) because disks were designed to function in the same way as tape drives. In this way, backup software applications developed to write data to tapes can be performed. VTL lost its popularity after backup software vendors upgraded their products to use direct disk instead of tape.
Continuous Data Protection
The Continuous Data Protection platform solves these problems completely. All initial backups are made to disk. Then perform an incremental backup every Minutes or seconds when data is created or edited. This type of backup can protect the entire data at all times and can protect all types of data.

Backup Appliance
In the early days of disk backup Backup software is designed to run on separate servers. This software synchronizes the backup process and writes the backup data to the storage disk. These systems quickly gained popularity as they acted as online backups. This means that data can be backed up or restored as needed. without having to connect tapes anymore
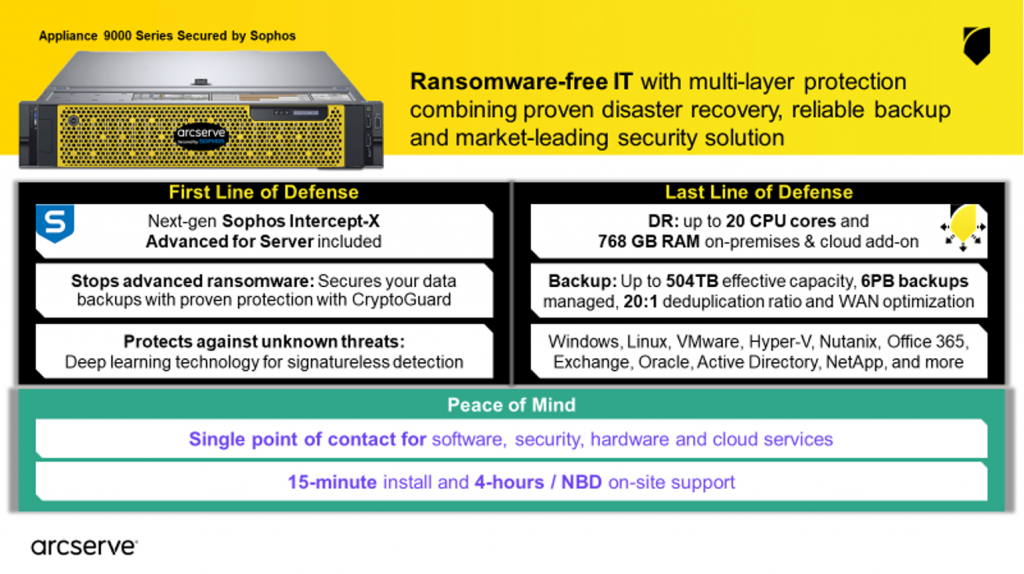
Although some backup products still use separate backup servers. Backup software system vendors are increasingly shifting to hardware backup protection and backup appliances. Backup hardware data device is the server on which the HDD is installed and backup software.
These plug and play storage devices often have an automatic feature for checking disk capacity. expandable storage and can connect to a pre-configured tape library
Hyper-converged Backup Appliance
Some backup vendors have begun to offer a single backup platform. Hyper-converged Backup Appliance based on the use of hyperconverged systems. These systems consist of a group of server nodes (clusters) that are grouped together and manage the overall backup-related processes.
One of the key benefits of a hyperconverged backup system is that it is easily scalable. Each node within a hyperconverged system contains built-in storage, compute, and network resources. Administrators can easily scale their organization’s reserve capacity. by adding a node to the cluster

Whether it’s hyperconverged or not Most disk backup devices allow copies to be moved from disk to magnetic tape for long-term storage. The magnetic tape system is still in use. Due to the increased tape capacity and the necessity of storing data for longer periods of time
Solid State Drive (SSD)
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are increasingly being used for backup purposes. But due to price and durability concerns, it may not be very popular. Some Backup Appliance vendors offer SSDs as caching or tiered tools for managing writes to disk arrays. This is a plus in terms of speed integration, especially in hyperconverged systems.
The data is initially cached in flash storage and then written to disk. As SSD vendors start producing SSDs with more capacity than disk drives This is useful for backups and can replace the disk in the future.
Cloud Storage
A backup that sends a copy of the data to another location. This may include company backup data centers or leased storage locations. offsite backup which at present there are more and more Equivalent to a cloud storage subscription as a service. which provides low cost scalable capacity and reduce the customer’s need to purchase and maintain spare hardware. and will be more popular
Offsite Backup
Modern backup software systems have evolved to provide stronger capabilities for backups. These features include Unlimited snapshot backup plans and tools for replicating snapshots to a backup center or even offsite backup. Data is transmitted over a high-bandwidth network connection or corporate intranet and can be restored to other locations.
Cloud Backup and Storage
Cloud backup It’s more popular and has a significantly lower price today. and is popular for making it a primary backup location and a secondary backup location (DR Site). Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS), which provides low cost scalable capacity and reduce the customer’s need to purchase and maintain spare hardware.
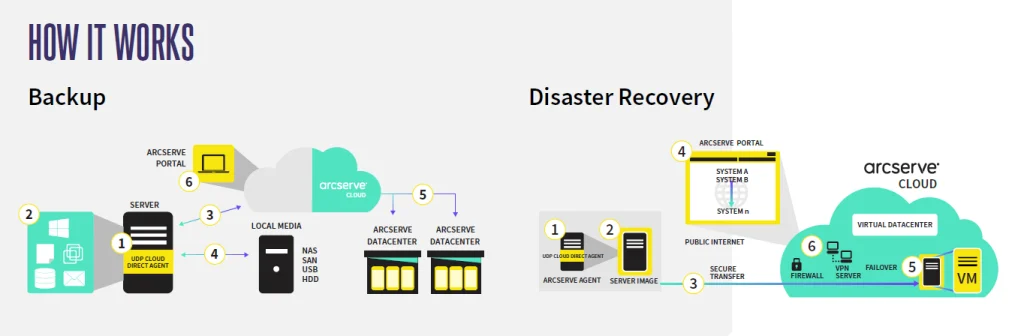
Cloud backups are divided into:
- Public Cloud Storage Users submit data to cloud service providers who charge a monthly subscription fee based on their used storage. There is an additional fee for data inbound and outbound, with AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure being the largest public cloud providers. There is also Small service providers that manage their cloud backups or manage customer backups on large public clouds.
- Private Cloud Storage The data is backed up to different servers. within the company firewall It is typically located between an on-premises data center and a backup data center (DR Site). For this reason, private cloud storage is sometimes referred to as a “detailed cloud storage”. Store data on the internal cloud.
- Hybrid Cloud Storage Companies use storage both on-site and off-premises. Organizations often choose public cloud storage for archiving and long-term retention. They use private storage (Private Cloud) for local access and backup for quick access to the most important data and needs.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)
Most backup software system vendors Additional services are available that allow user applications to be backed up to both the Public and Private Cloud to free up space on Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) customer storage. that when there is a catastrophic event that causes the customer’s system to crash or become unusable.
The backup software system can enable customer systems and applications to continue operating in the cloud and still be able to restore them back to their original systems.
Cloud-to-cloud (C2C) Backup
It is an alternative approach that has become increasingly popular. Backup Cloud-to-Cloud (C2C) is used to protect data on Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms such as Salesforce or Microsoft Office 365. These data usually only exist in the cloud.
But SaaS vendors often charge large fees to recover data lost due to customer errors. C2C backup works by copying SaaS data to another cloud. This makes it possible to recover if data is lost.
Backup and backup storage for PCs and mobile devices
PC users can consider either backing up local data from their computer’s internal hard disk drive to an attached external hard drive or to removable media such as a USB drive.
Another option for consumers is backing up data from smartphones and tablets to cloud storage. This is available from vendors such as Box, Carbonite, Dropbox, Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, and others.
These services are often used to provide some capacity for free. This gives consumers the option to purchase additional storage as needed. Unlike enterprise cloud storage offerings, these consumer cloud offerings generally do not provide the level of data security needed for businesses.
Vendors of backup software and hardware
- The Backup Appliance platform is sold by the following vendors:
- Arcserve Appliance, Barracuda Networks, Cohesity, Dell EMC (Data Domain), Drobo, ExaGrid Systems, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Hitachi Vantara, IBM, NEC Corp., Oracle StorageTek (ไลบรารีเทป), Quantum Corp., Rubrik, Spectra Logic, Unitrends และ Veritas NetBackup
- Vendors of enterprise backup software:
- Acronis, Arcserve, Asigra, Commvault, Datto, Dell EMC Data Protection Suite (Avamar และ NetWorker), Druva, Nakivo, Veeam Software และ Veritas Technologies



